JSON Export
JSON Export
Export your interactive story as clean, optimized JSON data designed for game engines and custom applications.
What is JSON Export?
JSON export converts your StoryFlow Editor project into a portable, engine-agnostic data format optimized for parsing and integration. Unlike HTML export which packages a complete runtime, JSON export provides pure data that you can load into any game engine or custom application.
Key Features:
- Text Extraction: All player-visible text moved to string tables for easy localization
- Clean Structure: Editor metadata stripped, only game-relevant data included
- Keyed Objects: Nodes and variables indexed by ID for O(1) lookup performance
- Hash-Based IDs: Collision-free variable identifiers support any character
- Cross-Platform Paths: Lowercase paths with forward slashes work everywhere
- Asset Management: Centralized asset registry with automatic file copying
Perfect For
- Unity, Godot, Unreal Engine integration
- Custom game engines and frameworks
- Non-game applications (chatbots, training tools)
- Multi-language support (localization-ready)
- Cross-platform deployment (Windows, Mac, Linux, Web, Mobile)
- Version control friendly (readable JSON with consistent formatting)
Design Philosophy
JSON export prioritizes performance, portability, and parsability. The format is designed to be loaded once at game start, with all lookups happening in O(1) time using dictionaries/maps. Special characters in names are handled via MD5 hashes, ensuring no collisions while preserving original text in localization tables.
How to Export
Export Steps:
- Open your project in StoryFlow Editor
- Ensure you have set a Startup Script via the menu next to the Play button (required for export)
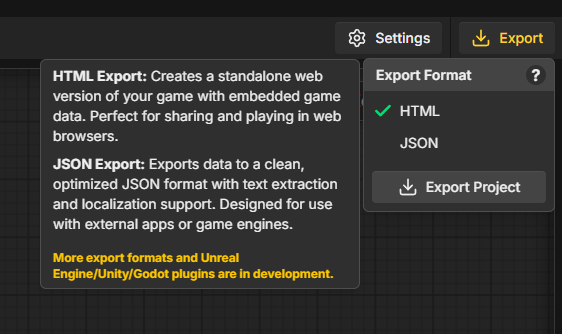
- Click the Export button in the top-right corner (amber download icon)
- In the dropdown menu, select JSON as the export format
- Click the Export Project button
- When complete, click Show in Folder to open the
build/directory
Build Folder Behavior
The build/ folder is located inside your project folder and is cleared before each export to ensure a clean state. Both HTML and JSON exports use the same output directory. Any manual edits will be overwritten on re-export.
File Structure
JSON export creates a build/ folder inside your project folder containing project metadata, scripts, variables, and assets.
build/
├── project.json
├── global-variables.json
├── chapter1/
│ ├── intro.json
│ └── dialogue.json
├── shared/
│ └── utilities.json
└── images/
└── characters/
├── hero.png
└── background.jpg
Path Normalization
All file paths are automatically normalized to lowercase with forward slashes for cross-platform compatibility. Script files (.sfe) are converted to .json extension, and the original folder structure from your content/ directory is preserved. For example, content/Chapter1/Intro.sfe becomes build/chapter1/intro.json. This ensures your exported project works identically on Windows, macOS, and Linux without path separator or case sensitivity issues.
Format Specification
project.json
The root project file containing metadata and the entry point script reference.
JSONCopy
{
"version": "1.0.0",
"apiVersion": "1.0",
"metadata": {
"title": "My First Project",
"description": "An interactive adventure game",
"created": "2025-01-15T10:30:00.000Z",
"modified": "2025-01-20T14:45:00.000Z"
},
"startupScript": "scripts/intro.json"
}
- version: StoryFlow Editor version (e.g.,
"1.0.0") - apiVersion: JSON API version for compatibility checking (currently
"1.0") - metadata: Project information (title, description, creation and modification timestamps)
- startupScript: Path to the initial script file (normalized, lowercase, forward slashes)
Script Files
Each script file represents a single flow graph with nodes, connections, and local data.
JSONCopy
{
"startNode": "0",
"nodes": {
"0": {
"type": "start",
"id": "0"
},
"8661543518ca4b7284337c6590833b96": {
"type": "dialogue",
"id": "8661543518ca4b7284337c6590833b96",
"title": "dlg_1_title",
"text": "dlg_2",
"choices": [
{
"id": "668948d5a45a4456abd5f0c4441ff3d5",
"text": "choice_3"
}
]
},
"9090f4ba47b8469dae82ff048322d585": {
"type": "runScript",
"id": "9090f4ba47b8469dae82ff048322d585",
"script": "scripts/next.json"
}
},
"connections": [
{
"id": "xy-edge__0source-0--8661...",
"source": "0",
"target": "8661543518ca4b7284337c6590833b96",
"sourceHandle": "source-0-",
"targetHandle": "target-8661543518ca4b7284337c6590833b96-"
}
],
"variables": {},
"strings": {
"en": {
"dlg_1_title": "Merchant",
"dlg_2": "Welcome to my shop!",
"choice_3": "Show me your wares"
}
},
"assets": {}
}
Key Fields:
- nodes: Dictionary of nodes keyed by ID for O(1) lookup (see Node Types)
- connections: Array of edges linking nodes together (see Connection Schema). Editor styling properties (color, animation) are removed.
- variables: Local variables defined in this script (see Variable Schema)
- strings: Localization table mapping string keys to display text (see Localization Support). Empty strings result in no property being set on the node, while whitespace-only strings are trimmed and result in empty string keys.
- assets: Asset references (images) used in this script (see Asset Schema)
Comment Nodes Excluded
Comment nodes are editor-only annotations and are not included in the JSON export. Only functional nodes that affect gameplay or story flow are exported.
Variable Scope in Nodes
Variable get/set nodes (getBool, setBool, getInt, setInt) include an optional isGlobal field. When true, the node references a global variable. When omitted or false, it references a local variable. This allows you to have both global and local variables with the same name without conflicts.
Conditional Node Input Resolution
Multi-input nodes (AND, OR, Equal (Boolean), Plus, Minus, Greater Than, Greater Than or Equal, Less Than, Less Than or Equal, Equal (Integer)) have value1 and value2 fields. These are fallback values used when no connection exists to that input handle. Important: value1 represents the TOP input handle (visually upper), and value2 represents the BOTTOM input handle (visually lower). Always check connections first - if an input handle has an incoming connection, evaluate that connected node instead of using the stored value. Branch nodes have a single value field instead of value1/value2. This design allows nodes to work both with visual connections and standalone checkbox/input values.
Global Variables
The global-variables.json file contains all global variables with hash-based IDs.
JSONCopy
{
"variables": {
"var_47c14840": {
"id": "var_47c14840",
"name": "var_1_name",
"type": "boolean",
"value": false
},
"var_cace59e2": {
"id": "var_cace59e2",
"name": "var_2_name",
"type": "integer",
"value": 0
}
},
"strings": {
"en": {
"var_1_name": "QuestCompleted",
"var_2_name": "PlayerHealth"
}
}
}
Hash-Based Variable IDs
Variable IDs are generated using MD5 hashing (first 8 characters) of the original variable name. This allows variables to have any name including spaces and special characters while guaranteeing no ID collisions. Original names are preserved in the strings table for display purposes.
Variable Types:
- boolean: True/false values for flags and conditions
- integer: Whole numbers for counters, stats, and quantities (no decimals)
API Reference
Comprehensive reference documentation for all schemas in the JSON export format.
File Schemas
Project File (project.json) Schema
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
version |
string | Yes | StoryFlow Editor version (e.g., "1.0.0") |
apiVersion |
string | Yes | JSON API version (currently "1.0") |
metadata |
object | Yes | Project metadata (title, description, created, modified) |
startupScript |
string | Yes | Path to startup script file (e.g., "scripts/main.json") |
Script File Schema
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
startNode |
string | Yes | Node ID to start execution from (always "0") |
nodes |
object | Yes | Dictionary of nodes keyed by node ID (see Node Types) |
connections |
array | Yes | Array of connection objects (see Connection Schema) |
variables |
object | Yes | Dictionary of local variables keyed by ID (see Variable Schema) |
strings |
object | Yes | Localization table for script text (see Localization Support) |
assets |
object | Optional | Dictionary of assets keyed by asset ID (see Asset Schema) |
global-variables.json Schema
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
variables |
object | Yes | Dictionary of global variables keyed by variable ID (see Variable Schema) |
strings |
object | Yes | Localization table for variable names (see Localization Support) |
Node Types
All nodes share a base structure with type and id fields. Additional fields vary by node type.
Start Node
Start
The entry point node. Every script must have exactly one start node with id "0".
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
type |
string | Yes | Node type ("start") |
id |
string | Yes | Must be "0" for start node |
Dialogue Node
Dialogue
Example Dialogue Node
Example Option
Condition
On Click
Displays text and options (choices) to the player. Supports optional title, image, and multiple options (choices) with conditions.
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
type |
string | Yes | Node type ("dialogue") |
id |
string | Yes | Unique node identifier |
title |
string | No | String key for dialogue title (references strings table) |
text |
string | No | String key for dialogue text (references strings table) |
image |
string | No | Asset key for dialogue image (references assets table) |
choices |
Choice[] | No | Array of choice objects (see Choice Schema) |
Set Boolean Node
SET
hasKey
Sets a boolean variable to a specific value or accepts input from another node.
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
type |
string | Yes | Node type ("setBool") |
id |
string | Yes | Unique node identifier |
variable |
string | Yes | Variable ID to set (e.g., "a1b2c3d4") |
value |
boolean | No | Hardcoded value. Omit to accept input from connected node |
isGlobal |
boolean | No | If true, variable is in global scope |
Get Boolean Node
hasKey
Retrieves the current value of a boolean variable.
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
type |
string | Yes | Node type ("getBool") |
id |
string | Yes | Unique node identifier |
variable |
string | Yes | Variable ID to retrieve (e.g., "a1b2c3d4") |
isGlobal |
boolean | No | If true, variable is in global scope |
NOT Boolean Node
NOT
Inverts a boolean value. Outputs the logical NOT of the input.
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
type |
string | Yes | Node type ("notBool") |
id |
string | Yes | Unique node identifier |
AND Boolean Node
AND
Performs logical AND operation on two boolean inputs. Returns true only if both inputs are true.
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
type |
string | Yes | Node type ("andBool") |
id |
string | Yes | Unique node identifier |
value1 |
boolean | No | Value used when this input handle has no incoming connection |
value2 |
boolean | No | Value used when this input handle has no incoming connection |
OR Boolean Node
OR
Performs logical OR operation on two boolean inputs. Returns true if at least one input is true.
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
type |
string | Yes | Node type ("orBool") |
id |
string | Yes | Unique node identifier |
value1 |
boolean | No | Value used when this input handle has no incoming connection |
value2 |
boolean | No | Value used when this input handle has no incoming connection |
Equal Boolean Node
==
Compares two boolean values for equality. Returns true if both inputs are the same.
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
type |
string | Yes | Node type ("equalBool") |
id |
string | Yes | Unique node identifier |
value1 |
boolean | No | Value used when this input handle has no incoming connection |
value2 |
boolean | No | Value used when this input handle has no incoming connection |
Branch Node
Branch
True
Condition
False
Conditional branching based on a boolean input. Routes execution to different paths.
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
type |
string | Yes | Node type ("branch") |
id |
string | Yes | Unique node identifier |
value |
boolean | No | Value used when condition handle has no incoming connection |
Run Script Node
Run Script
Select Script
Executes another script file, allowing for modular story organization and reusable subscripts.
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
type |
string | Yes | Node type ("runScript") |
id |
string | Yes | Unique node identifier |
script |
string | Yes | Path to script file (e.g., "content/chapter2.sfe") |
End Node
End
Marks the end of script execution. When reached, the story concludes or returns to caller.
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
type |
string | Yes | Node type ("end") |
id |
string | Yes | Unique node identifier |
Set Integer Node
SET
playerGold
Sets an integer variable to a specific value or accepts input from another node.
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
type |
string | Yes | Node type ("setInt") |
id |
string | Yes | Unique node identifier |
variable |
string | Yes | Variable ID to set (e.g., "a1b2c3d4") |
value |
number | No | Hardcoded value. Omit to accept input from connected node |
isGlobal |
boolean | No | If true, variable is in global scope |
Get Integer Node
playerGold
Retrieves the current value of an integer variable.
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
type |
string | Yes | Node type ("getInt") |
id |
string | Yes | Unique node identifier |
variable |
string | Yes | Variable ID to retrieve (e.g., "a1b2c3d4") |
isGlobal |
boolean | No | If true, variable is in global scope |
Plus Node
Adds two integer values together. Outputs the sum of the inputs.
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
type |
string | Yes | Node type ("plus") |
id |
string | Yes | Unique node identifier |
value1 |
number | No | Value used when this input handle has no incoming connection |
value2 |
number | No | Value used when this input handle has no incoming connection |
Minus Node
Subtracts the second input from the first. Outputs the difference.
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
type |
string | Yes | Node type ("minus") |
id |
string | Yes | Unique node identifier |
value1 |
number | No | Value used when this input handle has no incoming connection |
value2 |
number | No | Value used when this input handle has no incoming connection |
Greater Than Node
Compares two integer values. Returns true if the first input is greater than the second.
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
type |
string | Yes | Node type ("greaterThan") |
id |
string | Yes | Unique node identifier |
value1 |
number | No | Value used when this input handle has no incoming connection |
value2 |
number | No | Value used when this input handle has no incoming connection |
Greater Than or Equal Node
=
Compares two integer values. Returns true if the first input is greater than or equal to the second.
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
type |
string | Yes | Node type ("greaterThanOrEqual") |
id |
string | Yes | Unique node identifier |
value1 |
number | No | Value used when this input handle has no incoming connection |
value2 |
number | No | Value used when this input handle has no incoming connection |
Less Than Node
<
Compares two integer values. Returns true if the first input is less than the second.
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
type |
string | Yes | Node type ("lessThan") |
id |
string | Yes | Unique node identifier |
value1 |
number | No | Value used when this input handle has no incoming connection |
value2 |
number | No | Value used when this input handle has no incoming connection |
Less Than or Equal Node
<=
Compares two integer values. Returns true if the first input is less than or equal to the second.
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
type |
string | Yes | Node type ("lessThanOrEqual") |
id |
string | Yes | Unique node identifier |
value1 |
number | No | Value used when this input handle has no incoming connection |
value2 |
number | No | Value used when this input handle has no incoming connection |
Equal Integer Node
==
Compares two integer values for equality. Returns true if both inputs are the same.
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
type |
string | Yes | Node type ("equalInt") |
id |
string | Yes | Unique node identifier |
value1 |
number | No | Value used when this input handle has no incoming connection |
value2 |
number | No | Value used when this input handle has no incoming connection |
Connection Schema
Connections define the flow between nodes in the script graph.
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
id |
string | Yes | Unique connection identifier |
source |
string | Yes | Source node ID |
target |
string | Yes | Target node ID |
sourceHandle |
string | No | Source handle ID for nodes with multiple outputs (e.g., branch, dialogue options) |
targetHandle |
string | No | Target handle ID for nodes with multiple inputs (e.g., boolean operators) |
Variable Schema
Variables store persistent state across script execution. Variable IDs are MD5 hash-based identifiers (first 8 characters of the hash of the variable name).
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
id |
string | Yes | Variable ID (e.g., "a1b2c3d4" - first 8 chars of MD5 hash) |
name |
string | Yes | String key for variable display name (references strings table) |
type |
string | Yes | Variable type: "boolean" or "integer" |
value |
any | Yes | Default value (type matches variable type) |
Asset Schema
Assets define references to external image files used in the story.
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
id |
string | Yes | Unique asset identifier (e.g., "asset_elder_portrait") |
type |
string | Yes | Asset type: "image" |
path |
string | Yes | Relative path to asset file from build directory |
Choice Schema
Choices are options presented to the player in dialogue nodes. Each choice can have a condition and triggers an action when selected.
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
id |
string | Yes | Unique choice identifier |
text |
string | Yes | String key for choice text (references strings table) |
Parsing and Loading
This section explains how to integrate StoryFlow Editor's JSON export into external systems and game engines. The examples below demonstrate the recommended patterns for loading project data, building connection maps, and resolving variables at runtime.
Initial Load
Load the exported data in your game engine at startup. The recommended loading sequence is:
- Parse
[project.json](https://storyflow-editor.com/docs/json-export/#project-json)to get metadata and startup script path - Load
[global-variables.json](https://storyflow-editor.com/docs/json-export/#global-variables)into a runtime variable store - Load the startup script file referenced in
[project.json](https://storyflow-editor.com/docs/json-export/#project-json) - Pre-load additional scripts as needed for your use case
Loading Strategy
For small projects, load all scripts at startup. For large projects with hundreds of scripts, implement lazy loading where scripts are loaded on-demand when referenced by runScript nodes. Cache loaded scripts to avoid re-parsing.
Building Connection Maps
Build adjacency maps when loading each script to enable fast graph traversal. This converts the connections array into a dictionary structure for O(1) lookups.
JavaScriptCopy
// Example: Building an adjacency map
function buildConnectionMap(script) {
const map = new Map();
for (const connection of script.connections) {
if (!map.has(connection.source)) {
map.set(connection.source, []);
}
map.get(connection.source).push({
target: connection.target,
sourceHandle: connection.sourceHandle,
targetHandle: connection.targetHandle
});
}
return map;
}
// Usage: Get all outgoing connections from a node
const outgoing = connectionMap.get(currentNodeId) || [];
This pattern allows you to instantly find all nodes connected to the current node without iterating through the entire connections array.
Variable Resolution
Variables are referenced by their hash-based IDs in node data. Maintain separate stores for global and local variables, using the isGlobal flag in get/set nodes to determine which store to access.
JavaScriptCopy
// Example: Variable resolution with separate global/local stores
class VariableStore {
constructor(globalVariables) {
this.globalVars = new Map();
this.localVars = new Map();
// Load global variables
for (const [id, variable] of Object.entries(globalVariables.variables)) {
this.globalVars.set(id, variable.value);
}
}
loadScriptVariables(scriptVariables) {
// Clear local variables when loading a new script
this.localVars.clear();
// Load script-local variables
for (const [id, variable] of Object.entries(scriptVariables)) {
this.localVars.set(id, variable.value);
}
}
get(variableId, isGlobal = false) {
if (isGlobal) {
return this.globalVars.get(variableId);
}
return this.localVars.get(variableId);
}
set(variableId, value, isGlobal = false) {
if (isGlobal) {
this.globalVars.set(variableId, value);
} else {
this.localVars.set(variableId, value);
}
}
}
// Usage in a getBool node
const node = script.nodes['863fc74e828046daa020f6696fe60f2e'];
const value = variableStore.get(node.variable, node.isGlobal || false);
Variable Scope Resolution
Get/set nodes include an optional isGlobal field to indicate scope. When true, the variable should be looked up in global storage. When false or omitted, the variable is local to the current script. Your runtime implementation should maintain separate global and local variable stores, with the isGlobal flag determining which store to use. This allows both global and local variables to have identical hash-based IDs without conflicts.
Performance Optimization
The JSON export format is designed for maximum runtime performance. Follow these best practices:
- Dictionary Lookups: Nodes and variables are keyed objects, not arrays. Use direct lookups instead of iteration.
- Connection Caching: Build adjacency maps once at load time, reuse throughout execution.
- String Table Lookups: Cache localized strings at startup to avoid repeated lookups during gameplay.
- Lazy Script Loading: For large projects, load scripts on-demand when first referenced by runScript nodes.
- Asset Preloading: Parse asset references from scripts and preload required assets before execution.
Performance Profile
With proper implementation, node execution should run in O(1) time for lookups and O(E) time for traversal where E is the number of edges from the current node. Even projects with thousands of nodes execute efficiently.
Localization Support
StoryFlow Editor does not currently have built-in localization functionality, but the JSON export format was designed from the ground up to support multi-language projects. All player-facing text is extracted to string tables, making localization straightforward when you're ready to add it. Each file has a strings object with language codes as keys.
JSONCopy
"strings": {
"en": {
"dlg_1_title": "Merchant",
"dlg_2": "Welcome to my shop!",
"choice_3": "Show me your wares"
},
"es": {
"dlg_1_title": "Comerciante",
"dlg_2": "¡Bienvenido a mi tienda!",
"choice_3": "Muéstrame tus productos"
},
"ja": {
"dlg_1_title": "商人",
"dlg_2": "私の店へようこそ!",
"choice_3": "商品を見せてください"
}
}
Localization Workflow:
- Export your project to JSON (includes default language strings)
- Extract all string keys from strings objects across all files
- Send keys to translators or use translation tools
- Add translated strings to the strings objects with appropriate language codes
- Set the current language in your game settings
- Look up strings using the current language code at runtime
Language Fallback
Implement fallback logic where if a string key is missing in the selected language, fall back to the defaultLanguage specified in each file. This prevents missing text if translations are incomplete.
Related Topics
→ HTML Export→ Game Engine Integration→ Node Types→ Variables